What is Tibial Interlocking Nail and How Does it Work?
The Tibial Interlocking Nail is a critical innovation in orthopedic surgery. It provides a stable fixation option for tibial fractures, particularly in complex scenarios. According to a report by the Journal of Orthopedics, the use of interlocking nails has increased the success rate of tibial fracture healing by nearly 85%. This is significant, as tibial fractures account for about 25% of all long bone fractures.
The design of the Tibial Interlocking Nail allows for rotational stability. This feature can be vital for patients engaged in physical rehabilitation. However, despite these advantages, complications do exist. Some patients experience implant-related issues, such as infections or malalignment. A study presented at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons found that 10% of patients required further surgical intervention.
As the medical field evolves, the need for improved techniques remains. Continuous refinement of the Tibial Interlocking Nail is essential. This approach could reduce complications and enhance patient outcomes. Attention to detail in both design and surgical technique will lead to better overall results and minimize the risks involved.
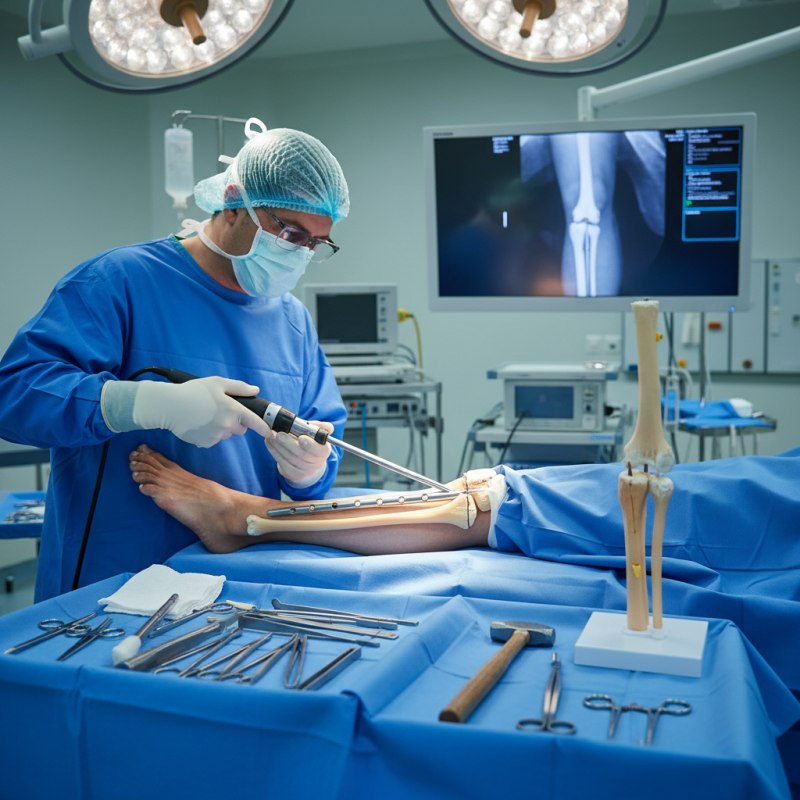
What is a Tibial Interlocking Nail?
A tibial interlocking nail is a specialized device used to stabilize fractures in the tibia, the main bone in your lower leg. This internal fixation method involves inserting a metal rod through the center of the tibia. The rod mimics the stability of the bone, promoting proper healing.
Studies show that tibial interlocking nails result in a high union rate, typically around 95%. The device allows doctors to align fractured bone fragments accurately. They can secure these fragments with screws that lock the nail in place. This technique minimizes movement at the fracture site, which is critical for recovery.
Tips: Always follow post-operative care instructions strictly. Staying active, as guided, can boost circulation and expedite healing. Regular follow-ups with your physician can help monitor the healing process effectively.
Despite the advantages, complications can occur. Some patients experience pain or infection around the nail site. These issues need addressing promptly. Not everyone is an ideal candidate for this device. A careful assessment is vital before surgery. Ensure adequate communication with your healthcare provider about all concerns.
Indications for Using Tibial Interlocking Nails
Tibial interlocking nails are essential in orthopedic surgery for stabilizing complex tibial fractures. The use of these nails has grown significantly, particularly in trauma cases. Approximately 75% of tibial fractures require surgery, and interlocking nails provide effective internal fixation.
Indications for using tibial interlocking nails include unstable fractures, non-unions, and fractures with significant soft tissue damage. A study published in the Journal of Orthopedic Trauma highlights a 90% success rate in healing when interlocking nails are used. This method is often preferred for its ability to enhance fracture stability while allowing for early weight-bearing.
However, not all cases benefit from this approach. Complications such as infection, malalignment, and implant failure can occur. Approximately 10% of patients report such issues. Surgeons must evaluate each situation carefully. Understanding the nuances of individual patient needs is crucial for optimal outcomes. Clear communication with patients about risks is essential.
Tibial Interlocking Nail Usage and Indications
The Surgical Procedure for Inserting a Tibial Interlocking Nail
The surgical procedure for inserting a tibial interlocking nail requires careful planning. The surgeon begins by assessing the patient's injury. Accurate imaging helps determine the best approach. Anesthesia is administered to ensure comfort during the surgery.
Once the patient is ready, an incision is made near the knee or ankle. The tibia is accessed, and a guide wire is inserted. This wire serves as a path for the nail. The interlocking nail is then carefully slid into place. It is crucial to ensure proper alignment. Misalignment can lead to complications later on.
After the nail is in position, locking screws are inserted. These screws stabilize the nail within the bone. This step is vital for successful healing. The surgeon will then close the incision. Monitoring begins post-surgery to check for signs of infection or complications.
Reflection on the procedure is essential. Every surgical step matters in ensuring optimal recovery. Adjustments might be needed in future cases based on outcomes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tibial Interlocking Nails
Tibial interlocking nails are a popular choice in orthopedic surgery. They aid in the stabilization of fractured tibias. The procedure is minimally invasive, leading to less soft tissue damage. Surgeons insert the nail through the bone and secure it with screws. This method allows for a quicker recovery time. However, it’s not without drawbacks.
One significant advantage is its effectiveness in promoting bone healing. Many patients report improved outcomes. The stability it provides is crucial in complex fractures. Additionally, patients often experience less postoperative pain compared to traditional methods. Yet, there are limitations to consider.
The procedure can sometimes lead to complications. Infection risk exists at the insertion site. Additionally, there's potential for improper alignment of the bone. This misalignment may require further corrective surgery. Long-term follow-up is essential for assessing healing progress. Despite these challenges, many find tibial interlocking nails to be a reliable option. While the benefits are clear, it's important to weigh them against the potential downsides.
Post-operative Care and Rehabilitation Following Tibial Nail Surgery
Post-operative care is crucial after tibial nail surgery. Patients should prioritize pain management immediately after the procedure. Discomfort may be present, but addressing it early can lead to better outcomes. Medication prescribed by the surgeon should be taken as directed. Monitoring for any unusual symptoms, like excessive swelling or fever, is essential. Communication with healthcare providers is key during this phase.
Rehabilitation begins soon after the surgery. Physical therapy typically starts within a few days. Gentle movements and exercises help improve blood circulation and prevent stiffness. Weight-bearing activities will be gradually introduced, depending on the patient's condition. Adapting to these changes can be challenging. Patients may feel frustrated at times. It’s normal to have ups and downs. Tracking progress can be motivating. Having a support system is also important. Friends and family can encourage recovery and provide necessary assistance.
What is Tibial Interlocking Nail and How Does it Work? - Post-operative Care and Rehabilitation Following Tibial Nail Surgery
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A tibial interlocking nail is an intramedullary device used to stabilize fractures of the tibia. |
| Indications | Indicated for complex tibial fractures, non-union, or as an internal fixation for other orthopedic conditions. |
| Procedure | Insertion of the nail is performed through a small incision, utilizing fluoroscopic guidance for precise placement. |
| Post-operative Care | Requires careful monitoring for infection, management of pain, and adherence to weight-bearing guidelines. |
| Rehabilitation | Physical therapy typically begins soon after surgery to promote mobility and strength in the affected leg. |
| Expected Outcome | Most patients achieve good functional recovery, with gradual return to normal activities within months. |