Exploring the Future of Innovation: How 3D Printers Are Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Design
The advent of the 3D printer has marked a transformative era in manufacturing and design, driving innovations across various industries. According to a report by SmarTech Analysis, the global 3D printing market is projected to reach $35.6 billion by 2024, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 23%. This surge can be attributed to the technology's ability to reduce production costs, shorten design cycles, and enable customized manufacturing solutions that were previously unimaginable.
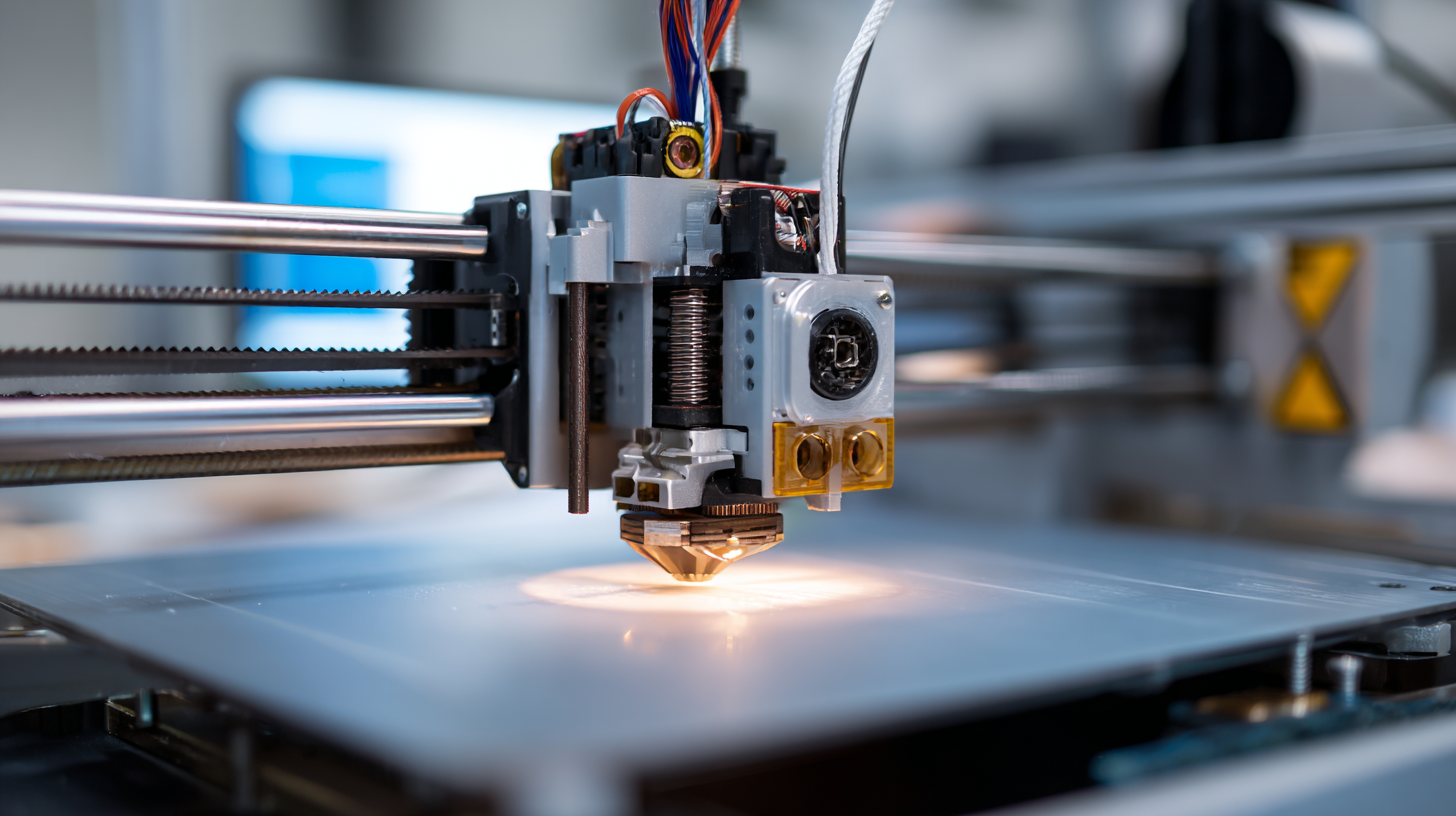
In aerospace, for example, companies like Boeing are leveraging 3D printing to produce lightweight components, resulting in significant fuel savings. Similarly, the healthcare sector is witnessing breakthroughs in personalized prosthetics and bioprinting of tissues. As we delve into the future of innovation, it becomes imperative to explore how 3D printers are not just reshaping traditional practices but also paving the way for new possibilities in design and production strategies.
The Evolution of 3D Printing Technology in Modern Manufacturing
The evolution of 3D printing technology has significantly transformed modern manufacturing processes, enhancing both design capabilities and production efficiency. Once a niche technology, 3D printing has now become an integral part of various industries, from aerospace to healthcare. Its ability to create complex and customized parts on demand has not only reduced material waste but also shortened product development cycles. This efficiency allows manufacturers to respond swiftly to market changes, enabling rapid prototyping and iterative design improvements.
Moreover, advancements in 3D printing materials and techniques are expanding its applications beyond traditional settings. Industries are increasingly utilizing 3D printing for producing end-use products, integrating innovative designs that would have been difficult or impossible to achieve through conventional manufacturing methods. As this technology continues to evolve, it is expected that its impact will further revolutionize design practices, paving the way for a new era of manufacturing that embraces automation and sustainability.
Exploring the Future of Innovation: 3D Printing in Manufacturing
This chart illustrates the growth in adoption of 3D printing technology across various industries from 2018 to 2023.
The Impact of 3D Printing on Design Flexibility and Customization
The advent of 3D printing technology has notably transformed manufacturing and design landscapes, particularly in terms of design flexibility and customization. Reports indicate that 3D printing applications are projected to grow significantly, with the market experiencing rapid advancements in various sectors such as automotive, fashion, and architecture. For instance, in the automotive industry, the introduction of custom components is increasingly becoming the norm, leading to more efficient production processes and a reduction in material waste.
A compelling example of 3D printing's flexibility is seen in the recent developments in bicycle manufacturing, where titanium components are being produced using advanced metal printing techniques. This method not only allows for lighter and stronger parts but also enables manufacturers to customize designs tailored to individual rider specifications. Similarly, innovations in boat manufacturing have led to the capability of producing entire 6-meter hulls autonomously in just 50 hours, underscoring how 3D printing can significantly shorten lead times while maintaining high levels of customization. The growing interest in sustainable practices within these industries further highlights 3D printing's potential to address market demands while promoting environmental responsibility.
Exploring the Future of Innovation: How 3D Printers Are Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Design - The Impact of 3D Printing on Design Flexibility and Customization
| Dimension | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Design Flexibility | Ability to create complex shapes and structures that were previously impossible. | Enhances creative freedom and innovation in various industries. |
| Customization | The capability to tailor products to meet individual customer needs. | Increases customer satisfaction and engagement by providing personalized solutions. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduction in material waste and lower manufacturing costs. | Improves profit margins and enables competitive pricing. |
| Speed of Production | Faster turnaround times from design to finished product. | Allows for rapid prototyping and quicker response to market demands. |
| Sustainability | Utilization of eco-friendly materials and reduction of carbon footprint. | Supports global sustainability goals and attracts environmentally conscious consumers. |
Sustainability and Efficiency: 3D Printing's Role in Eco-Friendly Manufacturing
As the world grapples with environmental challenges, 3D printing emerges as a beacon of sustainability in the manufacturing sector. Traditional manufacturing often involves significant waste, from excessive material use to the energy consumed in transportation. In contrast, 3D printing is an additive process, meaning it creates objects layer by layer, which drastically reduces material waste and allows for precise control over production. Moreover, this technology often enables the use of recycled materials, contributing to a more circular economy.
Tip: To maximize the sustainability of your 3D printing endeavors, consider using biodegradable filaments or experimenting with recycled plastics. This not only enhances your eco-friendliness but also sets a precedent for responsible manufacturing practices.
Efficiency is another striking benefit of 3D printing. By streamlining the production process, businesses can prototype and produce components faster than ever before, reducing time-to-market and cutting costs. Furthermore, on-demand printing eliminates the need for bulky inventories, which lessens the ecological footprint of storage and logistics.
Tip: Embrace digital inventory management alongside your 3D printing strategy to optimize production and minimize waste. This approach ensures that you only produce what you need, further amplifying the sustainability efforts in your manufacturing processes.
Real-World Applications of 3D Printing Across Industries
3D printing technology is making significant strides across various industries, fundamentally changing how products are designed and manufactured. According to a report by Wohlers Associates, the global 3D printing market is expected to reach $35.6 billion by 2024, highlighting the technology's increasing importance in sectors ranging from healthcare to aerospace. In the medical field, 3D printing is being used to create customized prosthetics and implants, allowing for personalized patient care that was previously unimaginable. For instance, surgeons can now print patient-specific anatomical models to practice complex procedures, improving surgical outcomes and reducing operation times.
In the automotive industry, companies like Ford and BMW are leveraging 3D printing for rapid prototyping and the production of lightweight components. This innovation not only accelerates the design process but also enhances production efficiency. A study by McKinsey indicates that 3D printing could save manufacturers up to 90% on their supply chain costs due to the reduction of waste and material usage. This transformative technology is not just a trend; it represents a paradigm shift in how products are conceived and made, enabling companies to bring innovative solutions to market faster than ever before.

Future Trends: What Lies Ahead for 3D Printing and Innovation
The SLS 3D printing market is poised for significant growth, projected to expand from a valuation of $1.353 billion in 2023 to an impressive $2.8118 billion by 2032. This translates to a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5%, indicating a robust demand for advanced manufacturing solutions. As industries increasingly adopt 3D printing technologies, particularly selective laser sintering (SLS), the potential applications continue to broaden, fueling innovation in product design and development.
This growth is driven by several factors, including the need for rapid prototyping, customized solutions, and sustainable manufacturing practices. Companies are exploring ways to leverage SLS technology to create more efficient supply chains and reduce material waste. The future trends in 3D printing suggest an evolution not only in hardware and software but also in the materials being used, further enhancing the capabilities of manufacturers to meet the dynamic market needs.
As investments in this sector increase, the innovations driven by 3D printing will undoubtedly reshape the landscape of manufacturing and design in the years to come.
Related Posts
-

Unlocking the Secrets to the Best 3D Systems Printers for Your Business Needs
-

The Future of Creating Innovative Solutions with the Best 3D Machine Printer
-
Exploring the Industry Standards for the Best 3D Printer and Their Impact on Your Business
-

Elevating Global Standards: How China's Top 3D Printers Redefine Business Quality
-
Innovative Solutions for Optimizing Your Best 3D Printing Machine Performance
-

Revolutionizing Prototyping: How 3D Systems Printers Are Transforming Manufacturing Efficiency