Best 3D Printers for Metal What to Consider Before Buying?
In recent years, the demand for a reliable 3D printer for metal has surged in various industries. Experts like Dr. Sarah J. Lum, a leading researcher in additive manufacturing, emphasize, “The right 3D printer for metal can revolutionize production efficiency.” As technology advances, more options are available, but not all are ideal for every application.
When considering a 3D printer for metal, several factors come into play. It's crucial to evaluate the printer's material capabilities, build size, and precision. Some models excel in speed, while others focus on intricate designs. Buyers can be overwhelmed by the choices, leading to decisions that may not meet specific needs.
While the potential is vast, one must be cautious. Many prints may fail due to poor settings or incorrect materials. Investing in a 3D printer for metal requires careful thought and sometimes, painful trial and error. Understanding one's requirements is essential to avoid pitfalls and ensure a perfect fit for your project.

Key Features of Metal 3D Printers to Evaluate
When considering metal 3D printers, several key features demand attention. First, the printing technology used is crucial.
Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
and
Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
are popular choices, each with distinct advantages. SLM offers high resolution and fine details, while EBM excels in thicker layers and faster speeds. According to recent market reports, the global metal 3D printing industry is expected to reach $2.5 billion by 2026, emphasizing the importance of choosing the right technology.
Material compatibility is another vital factor. Various alloys are used, including titanium, stainless steel, and aluminum. Each material has unique properties, altering the final product's performance and cost. Current research indicates that titanium-based prints can be up to 40% lighter than steel, making them ideal for aerospace applications. However, sourcing these materials could be challenging due to supply fluctuations, pushing manufacturers to rethink their strategies.
Lastly, post-processing requirements shouldn't be overlooked. Many metal prints need additional work, such as heat treatment or surface finishing, to achieve optimal strength. This can increase production time and costs. Knowing these factors helps in making informed decisions while navigating the evolving landscape of metal 3D printing.
Types of Metal 3D Printing Technologies Explained
Metal 3D printing technologies are diverse and evolving. Each type offers unique benefits. Understanding these is crucial before making a purchase. The most common technologies include Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), and Binder Jetting.
Selective Laser Melting uses a laser to fuse metal powder into solid parts. It's perfect for complex geometries. According to industry reports, it provides high precision and superior mechanical properties. Users often share concerns about the high cost of production. Maintenance of the equipment is another issue.
Binder Jetting offers a different approach. It uses a binding agent to join powder particles. This method is faster and more cost-effective. However, post-processing is required to achieve desired strength. Some end-users find this a challenge. Each technology has its pros and cons, making it essential to evaluate your specific needs.
Best 3D Printers for Metal: What to Consider Before Buying?
| Printer Type | Printing Method | Material Compatibility | Build Volume (mm) | Layer Resolution (μm) | Price Range ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Powder Bed Fusion | Selective Laser Melting (SLM) | Stainless Steel, Titanium | 250 x 250 x 300 | 50 | 100,000 - 300,000 |
| Binder Jetting | Binder Jet 3D Printing | Aluminum, Copper | 300 x 200 x 200 | 100 | 50,000 - 150,000 |
| Directed Energy Deposition | Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS) | Nickel, Titanium alloys | 500 x 500 x 500 | 75 | 200,000 - 500,000 |
| Fused Filament Fabrication | Metal Filament Extrusion | Bronze, Steel | 300 x 300 x 400 | 200 | 1,000 - 3,000 |
Material Compatibility for Metal 3D Printing
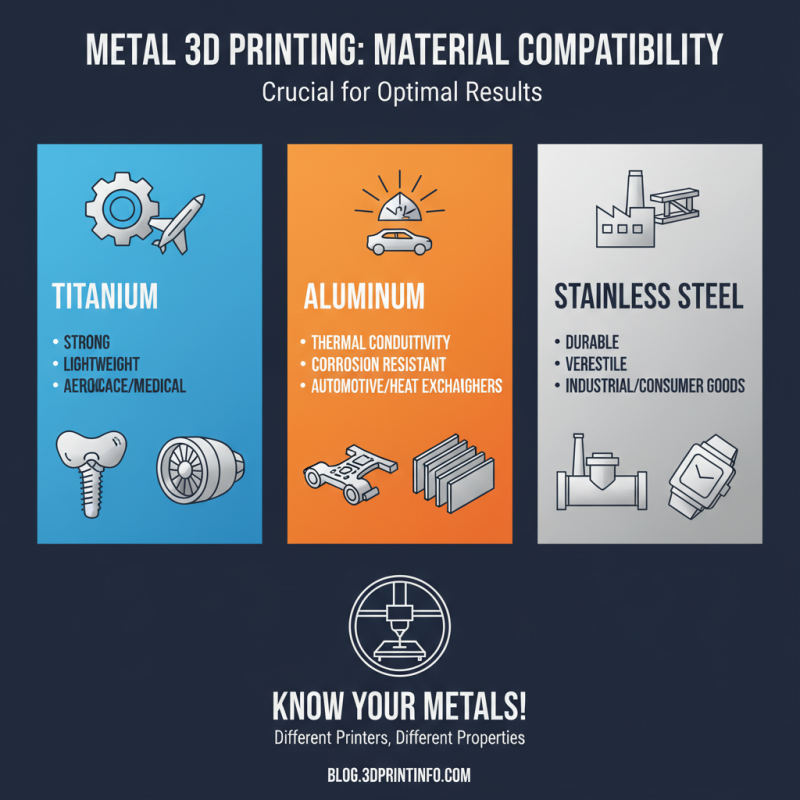
Material compatibility is crucial in metal 3D printing. Different printers work with various types of metals. Common materials include titanium, aluminum, and stainless steel. Each metal has unique properties that affect the printing process. For instance, titanium is strong yet lightweight. Aluminum is valued for its thermal conductivity. Understanding these differences is vital for optimal results.
Recent industry reports indicate that metal 3D printing is experiencing rapid growth. In 2022, it was estimated to reach $1.5 billion, with significant annual growth projected. This increase highlights the importance of selecting the right materials for specific applications. Misalignment in material choice can lead to weak structures. Poor adhesion and defects often stem from incompatible materials, impacting the overall integrity of the print.
User experience varies widely in this domain. Many users report challenges with specific alloys. Some materials require precise temperature control. Others may struggle with layer bonding. These factors can lead to trial-and-error approaches, which may not be ideal. Careful consideration of material compatibility can mitigate these issues and enhance printing efficiency.
Cost Considerations and Budgeting for Metal Printers
When considering a metal 3D printer, budgeting is crucial. Metal printers can vary in price significantly. Some start at a few thousand dollars, while others may cost over a hundred thousand. Be realistic about what you can afford. Determine if you need a high-end machine or a more affordable option.
Think about additional costs that might arise. Material costs can add up quickly. Metal powders are not cheap and can affect your overall budget. Maintenance and operational costs are also important. A high-end printer might require costly upkeep. Consider finding a balance between quality and affordability to suit your needs.
Moreover, purchasing a metal printer often involves indirect costs. Training staff on new equipment can take time and resources. These factors should be part of your financial plan. Proper research is vital before making a decision. A cheaper printer may not meet your needs and could lead to frustration later. It’s essential to evaluate every aspect carefully before investing.
Maintenance and Support for Metal 3D Printers
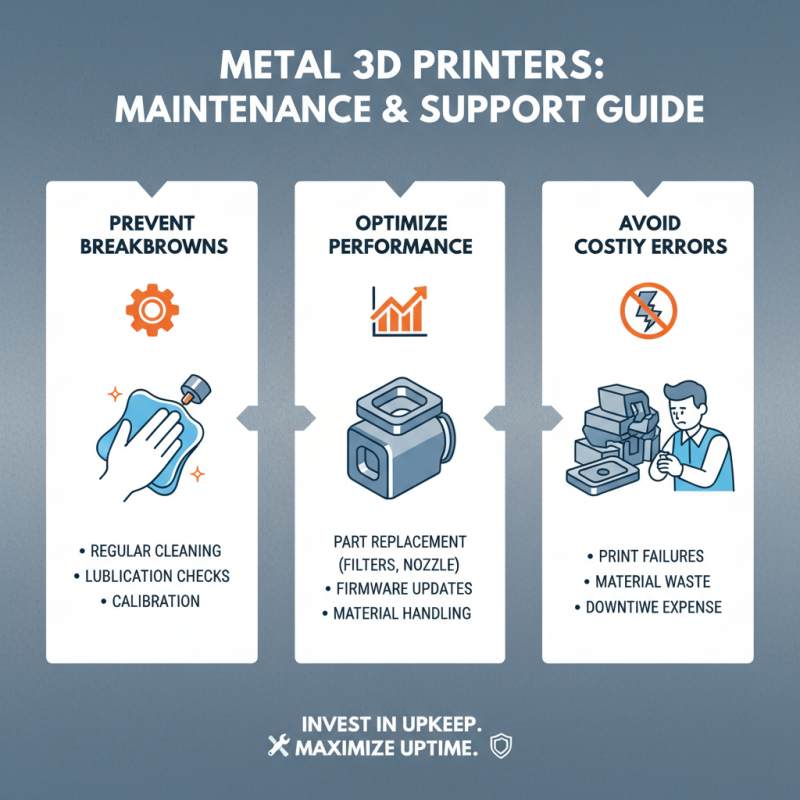
When considering metal 3D printers, maintenance and support are crucial factors. Regular upkeep can prevent costly breakdowns. Ensure you understand the cleaning procedures and part replacements required. Missteps in maintenance can lead to print failures and wasted materials.
Tips: Always keep your printer manual handy. Document your maintenance history. This will help in troubleshooting.
Support is just as important. Research available customer service options. A reliable support system can save you time and frustration. If something goes wrong, responsive support is invaluable.
Tips: Test out the support system before a purchase. Ask questions and gauge response times. This can predict future experiences.
Investing in a metal 3D printer is a commitment. Be prepared for both routine maintenance and potential support needs. It's not always straightforward, so reflection on your processes is essential. Consider your production goals and how maintenance aligns with them.
Related Posts
-

10 Key Factors to Choose the Best 3D Printer for Metal: Insights from 2023 Industry Trends
-

Challenges Faced by Businesses Using Industrial Metal 3D Printers
-

Digital Insights and Tips for Choosing the Best Industrial 3D Printer
-
Exploring Distinct Features of Industrial 3D Printers and Their Applications in Manufacturing
-

Top 10 Enclosed 3D Printers for Safe and High Quality Printing
-

10 Essential Tips for Mastering High Temperature 3D Printing Success